Bursitis Ball Of Foot Treatments
The most common bursa to be inflamed in the foot is the retrocalcaneal bursa (also referred to as the subtendinous calcaneal bursa). Located between the Achilles tendon and the heel bone (calcaneus), this is a "true" bursa that is present from birth. It acts as a cushion to protect the Achilles tendon from friction against the heel bone. Also commonly affected, the subcutaneous calcaneal bursa (also referred to as the Achilles bursa), located between the Achilles tendon and the skin, sits a little lower down the ankle towards the heel than the retrocalcaneal bursa. This bursa develops as you age, an "adventitious" bursa, to protect the tendon from friction at the back of the heel.
Causes
Improper foot wear, tight shoes or shoes that do not fit properly can cause extra pressure and friction on the back of the heel. Overtime, this pressure causes irritation of the bursae that protects the Achilles tendon causing one or both to swell and become inflamed. Athletes who overtrain or runners that increase their distance to quickly are at greater risk of experiencing Achilles bursitis. With over use, the Achilles bursae and tendon can become irritated and inflamed leading to thickening of the bursae lining and wearing of the tendon. Fluid builds in the bursa when it becomes irritated causing swelling of the Achilles bursa and pain at the back of the heel.
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of heel bursitis? pain, swelling, tenderness, redness, and/or warmth at either the bottom of the heel or top of the heel, depending on the degree of swelling, pain may be a dull ache or substantial enough to cause limping, running, jumping, and walking activities may exacerbate pain, wearing poorly fitting, tight, or high-heeled shoes may exacerbate pain.
Diagnosis
The doctor will discuss your symptoms and visually assess the bones and soft tissue in your foot. If a soft tissue injury is suspected, an MRI will likely be done to view where and how much the damage is in your ankle. An x-ray may be recommended to rule out a bone spur or other foreign body as the cause of your ankle pain. As the subcutaneous bursa is close to the surface of the skin, it is more susceptible to septic, or infectious, bursitis caused by a cut or scrape at the back of the heel. Septic bursitis required antibiotics to get rid of the infection. Your doctor will be able to determine whether there is an infection or not by drawing a small sample of the bursa fluid with a needle.
Non Surgical Treatment
Here are some of the most effective treatments for infracalcaneal bursitis Temporarily avoiding weight-bearing activities that put stress or strain on the heel bone can very helpful in treating infracalcaneal bursitis. PRICE (protection, rest, hot/cold contrast compresses, compression, and elevation) is another good acute management technique for this foot problem. Changing footwear is an effective long-term prevention and treatment tool for infracalcaneal bursitis. Shoes that possess a flat support base from heel to toe, a sufficiently wide toe box to accommodate natural toe splay, and a flexible sole that can be easily bent or twisted are best for preventing and managing infracalcaneal bursitis. An integrated approach to this problem usually involves the use of padded socks or heel cups to help reduce pressure, friction, and inflammation under the heel. Natural anti-inflammatory agents can also be helpful in quelling inflammation, reducing pain, and improving treatment times for infracalcaneal bursitis. In rare cases, more aggressive treatment methods may be required, such as cortisone injections or surgery to drain the bursal sac. Always consult your physician before beginning any healthcare regimen designed to treat infracalcaneal bursitis.
Prevention
Once your pain and inflammation is gone, you can prevent retrocalcaneal bursitis deformity by wearing the best shoes for your foot type. You should high-heels and pumps if possible. Wear orthotics (custom arch supports) or over-the-counter orthotic devices. Perform frequent Achilles tendon stretching exercises to prevent it from becoming tight agian. Avoiding running uphill when training. Try to run on softer surfaces and avoid concrete.
Hammer Toe Repair Surgery
A Hammer toe is a deformity of the second, third or fourth toes. In this condition, the toe is bent at the middle joint, so that it resembles a hammer. Initially, hammer toes are flexible and can be corrected with simple measures but, if left untreated, they can become fixed and require surgery. People with hammer toe may have corns or calluses on the top of the middle joint of the toe or on the tip of the toe. They may also feel pain in their toes or feet and have difficulty finding comfortable shoes.
Causes
Your toe contains two joints that allow it to bend at the middle and bottom. A hammertoe occurs when the middle joint becomes dislocated. Common causes of this joint dislocation include a toe injury, arthritis, a high foot arch, wearing shoes that don?t fit properly, tightened ligaments or tendons in the foot, pressure from a bunion (when your big toe points inward toward your second toe) Spinal cord or peripheral nerve damage may cause all of your toes to curl downward.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
If the toes remain in the hammertoe position for long periods, the tendons on the top of the foot will tighten over time because they are not stretched to their full length. Eventually, the tendons shorten enough that the toe stays bent, even when shoes are not being worn. The symptoms of hammertoe include a curling toe, pain or discomfort in the toes and ball of the foot or the front of the leg, especially when toes are stretched downward, thickening of the skin above or below the affected toe with the formation of corns or calluses, difficulty finding shoes that fit well. In its early stages, hammertoe is not obvious. Frequently, hammertoe does not cause any symptoms except for the claw-like toe shape.
Diagnosis
The treatment options vary with the type and severity of each hammer toe, although identifying the deformity early in its development is important to avoid surgery. Your podiatric physician will examine hammertoe and X-ray the affected area and recommend a treatment plan specific to your condition.
Non Surgical Treatment
Wear sensible shoes. If you don?t want to have surgery to fix your hammertoe, use non-medicated padding along with proper shoes made with a wider and deeper toe box to accommodate your foot?s shape. Ensuring your shoes have a good arch support can slow the progression of the condition as well. Use a pumice stone. The corn or callus that forms on top of the hammertoe can cause discomfort when you wear shoes. Treat the corn by using a file or pumice stone to reduce its size after a warm bath, then apply emollients to keep the area softened and pliable. Use silicone or moleskin padding on top of the area when wearing shoes. Do foot exercises. Theoretically, exercises like extending, then curling the toes, splaying the toes, and moving the toes individually may help prevent the digital contracture that causes hammertoe. Try these suggestions and see what works best for you.
Surgical Treatment
Sometimes surgery can not be avoided. If needed, the surgery chosen is decided by whether we are dealing with a flexible or rigid hammer toe. If the surgery is on a flexible hammer toe, it is performed on soft tissue structures like the tendon and or capsule of the flexor hammer toe. Rigid hammer toes need bone surgeries into the joint of the toe to repair it. This bone surgery is called an arthroplasty.
 Prevention
Prevention
As long as hammertoe causes no pain or any change in your walking or running gait, it isn?t harmful and doesn't require treatment. The key to prevention is to wear shoes that fit you properly and provide plenty of room for your toes.
The Cause Of Bunions?
Overview
 A simple bunion is an abnormal bump of bone that is formed at the head of our old friend, the first metatarsal bone. The bunion can either be on the top or side of the first metatarsal bone. In a more advanced bunion deformity, called Hallux Abducto Valgus, there starts to be a movement of the big toe toward the second toe. The most severe bunion is when the first toe not only moves toward the second toe, but it overlaps or underlaps the second toe. Bunions can cause swelling of the feet to occur.
A simple bunion is an abnormal bump of bone that is formed at the head of our old friend, the first metatarsal bone. The bunion can either be on the top or side of the first metatarsal bone. In a more advanced bunion deformity, called Hallux Abducto Valgus, there starts to be a movement of the big toe toward the second toe. The most severe bunion is when the first toe not only moves toward the second toe, but it overlaps or underlaps the second toe. Bunions can cause swelling of the feet to occur.
Causes
Shoes. The primary cause of bunions is the long term use of shoes, particularly tight-fitting shoes with pointed toes, or high heeled shoes. A study that examined people in cultures that do not wear shoes found no cases of bunions. Genetic. People who have misaligned toes or feet, are flatfooted with feet that roll inwards (over pronation), excessive flexibility of ligaments, abnormal bone structure, or have mechanical instability in the big toe joint are more susceptible to bunions. This is especially common when bunions occur in children or young adults. Injuries or other trauma (sprains, fractures or nerve injuries), neuromuscular disorders (polio or Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease), or limb-length discrepancies (one leg longer than the other). Repetitive stresses to the foot. Bunions are common in ballet dancers and in a few sports. Arthritis.
Symptoms
The skin over your big toe may be red and tender. Wearing any type of shoe may be painful. This joint flexes with every step you take. Your big toe may angle toward your second toe, or even move all the way under it. The skin on the bottom of your foot may become thicker and painful. Pressure from your big toe may force your second toe out of alignment, sometimes overlapping your third toe. If this condition gets severe, it may be difficult to walk. Your pain may become chronic and you may develop arthritis.
Diagnosis
Bunions are readily apparent - the prominence is visible at the base of the big toe or side of the foot. However, to fully evaluate the condition, the foot and ankle surgeon may take x-rays to determine the degree of the deformity and assess the changes that have occurred. Because bunions are progressive, they don?t go away, and will usually get worse over time. But not all cases are alike - some bunions progress more rapidly than others. Once your surgeon has evaluated your bunion, a treatment plan can be developed that is suited to your needs.
Non Surgical Treatment
Bunions can be treated conservatively (without surgery) using simple measures such as well-fitting shoes, orthoses simple painkillers and padding. Physiotherapy can help improve associated muscle imbalances. Such measures will not correct or even stop the deformity but they can help with symptoms. When non-surgical treatments prove insufficient, surgery can relieve your pain, correct any related foot deformity and help you resume your normal activities. 
Surgical Treatment
Bunions are painful deformities that develop when your big toe and first metatarsal slide out of alignment. Most of the time, this condition can be managed and your pain relieved using entirely conservative measures. Since this is a bone deformity, however, the problem can?t be truly corrected without a surgical procedure. Surgery for bunions realigns the displaced bones and restores the foot?s normal function.
What Actually Will Cause Feet To Over Pronate
Pronation is a normal motion that our feet make as they walk. With each step, the heel touches the ground first, then the foot rolls forward to the toes, causing the ankle to roll inward slightly and the arch to flatten out. That?s normal. But when that rolling inward becomes more pronounced, that?s over-pronation, which is a big problem. You can usually see over-pronation by looking at the back of the leg and foot. The Achilles tendon normally runs straight down from the leg to the foot, hitting the floor at a perpendicular angle. In feet that over-pronate, the Achilles tendon will be at a slight angle to the ground and the ankle bone will appear more prominent than usual.
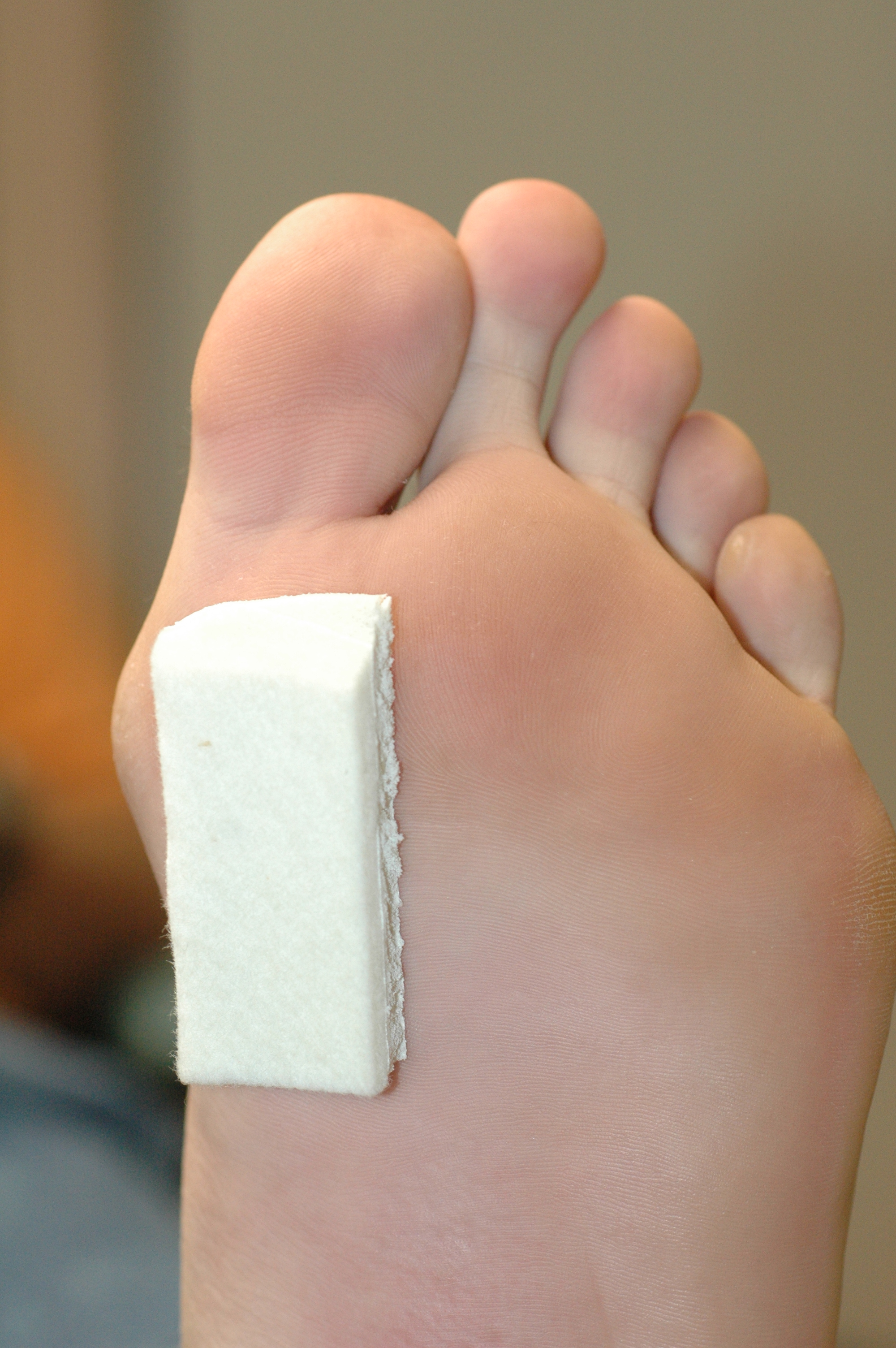
Causes
There has been some speculation as to whether arch height has an effect on pronation. After conducting a study at the Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology, Maggie Boozer suggests that people with higher arches tend to pronate to a greater degree. However, the generally accepted view by professionals is that the most pronation is present in those with lower arch heights. To complicate matters, one study done by Hylton Menz at the University of Western Sydney-Macarthur suggests that the methods for measuring arch height and determining whether someone is ?flat-footed? or ?high-arched? are unreliable. He says, ?For this reason, studies investigating the relationship between static arch height motion of the rearfoot have consistently found that such a classification system is a poor predictor of dynamic rearfoot function.
Symptoms
Symptoms can manifest in many different ways. Here is a list of some of the common conditions associated with over-pronation in children. Achilles Pain. Ankle pain. Arch Pain. Low back pain. Heel Pain. Knee Pain (Runner's knee and Chondromalecia of the patella) Osgood Schlatter Disease (pain below the knee) Shin Splints (pain in the front of the lower leg) Over-pronation does not necessarily mean your child has "flat feet." Even though children's arches may be relatively high when they lie down or sit, over-pronation may not be seen until your child is standing. A certain amount of pronation is normal. During normal walking or running ("gait cycle"), the heel strikes the ground and the foot rolls inward to absorb shock and adapt to the surface. This gait cycle is even more important if the running surface is uneven.
Diagnosis
So, how can you tell if you have overpronation, or abnormal motion in your feet, and what plantar fasciitis treatment will work to correct it? Look at your feet. While standing, do you clearly see the arch on the inside of your foot? If not, and if the innermost part of your sole touches the floor, then your feet are overpronated. Look at your (running/walking) shoes. If your shoes are more worn on the inside of the sole in particular, then pronation may be a problem for you. Use the wet foot test. Wet your feet and walk along a section of pavement, then look at the footprints you leave behind. A normal foot will leave a print of the heel connected to the forefoot by a strip approximately half the width of the foot on the outside of the sole. If you?re feet are pronated there may be little distinction between the rear and forefoot.

Non Surgical Treatment
Adequate footwear can often help with conditions related to flat feet and high arches. Certified Pedorthists recommend selecting shoes featuring heel counters that make the heel of the shoe stronger to help resist or reduce excessive rearfoot motions. The heel counter is the hard piece in the back of the shoe that controls the foot?s motion from side-to-side. You can quickly test the effectiveness of a shoe?s heel counter by placing the shoe in the palm of your hand and putting your thumb in the mid-portion of the heel, trying to bend the back of the shoe. A heel counter that does not bend very much will provide superior motion control. Appropriate midsole density, the firmer the density, the more it will resist motion (important for a foot that overpronates or is pes planus), and the softer the density, the more it will shock absorb (important for a cavus foot with poor shock absorption) Wide base of support through the midfoot, to provide more support under a foot that is overpronated or the middle of the foot is collapsed inward.
Prevention
Strengthen the glutes to slow down the force of the foot moving too far inward. Most individuals who over-pronate have weak glute muscles and strengthening this area is a must. A simple exercise to strengthen glutes is lateral tube walking across a field/court/room. Place a lateral stretch band around your ankles and move your leg sideways while keeping your feet forward.
Will Calcaneal Apophysitis Need Surgery Treatment?
Sever's disease, also called calcaneal apophysitis, is a painful bone disorder that results from inflammation (swelling) of the growth plate in the heel. A growth plate, also called an epiphyseal plate, is an area at the end of a developing bone where cartilage cells change over time into bone cells. As this occurs, the growth plates expand and unite, which is how bones grow.
Causes
Heel pain is very common in children because of the very nature of their growing feet and legs. In children, the heel bone (the calcaneus) is not fully developed until the age of 14 or older. Until then, new bone is forming at the growth plate of the foot (the apophysis, located at the back of the heel), an area which is softer than others due to its role in accommodating the growth. Repetitive stress on the growth plate due to walking, running and sports causes inflammation in the heel area. Because the heel's growth plate is sensitive, repeated running and pounding on hard surfaces can result in pediatric heel pain. Children and adolescents involved in football, soccer, running or basketball are especially vulnerable. Over-pronation (fallen arches and rolling inwards of the feet) will increase the stress on the growth plate and is therefore a significant cause and a major contributing factor to heel pain in children.
Symptoms
Pain is reproduced through a gentle squeeze of the back of the heel. Children may present with a limp or ?Bouncy gait?. Pain is worse barefoot and often present in the mornings and post exercise. The pain is located at the back of the heel, with localized swelling of the area.
Diagnosis
A doctor or other health professional such as a physiotherapist can diagnose Sever?s disease by asking the young person to describe their symptoms and by conducting a physical examination. In some instances, an x-ray may be necessary to rule out other causes of heel pain, such as heel fractures. Sever?s disease does not show on an x-ray because the damage is in the cartilage.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment may consist of one or more of the following, Elevating the heel, Stretching hamstring and calf muscles 2-3 times daily, Using R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), Foot orthotics, Medication, Physical therapy, Icing daily (morning), Heating therapy, Open back shoe are best and avoid high heel shoe. The Strickland Protocol has shown a positive response in patients with a mean return to sport in less than 3 weeks.
Prevention
Can Calcaneal Apophysitis Be Prevented? The chances of a child developing heel pain can be reduced by avoiding obesity. Choosing well-constructed, supportive shoes that are appropriate for the child?s activity. Avoiding or limiting wearing of cleated athletic shoes. Avoiding activity beyond a child?s ability.
What Are The Causes Of A Ruptured Achilles Tendon?
Overview
 The Achilles' tendon is located in the leg just behind and above the heel. As the connection between the heel and calf muscle, its function is to allow the bending of the foot downwards. Generally if there is a tear to the Achilles' tendon it will be known as a rupture. This can be a partial tear or a complete tear, although partial tears are much rarer.
The Achilles' tendon is located in the leg just behind and above the heel. As the connection between the heel and calf muscle, its function is to allow the bending of the foot downwards. Generally if there is a tear to the Achilles' tendon it will be known as a rupture. This can be a partial tear or a complete tear, although partial tears are much rarer.
Causes
Your Achilles tendon helps you point your foot downward, rise on your toes and push off your foot as you walk. You rely on it virtually every time you move your foot. Rupture usually occurs in the section of the tendon located within 2.5 inches (6 centimeters) of the point where it attaches to the heel bone. This section may be predisposed to rupture because it gets less blood flow, which may impair its ability to heal. Ruptures often are caused by a sudden increase in the amount of stress on your Achilles tendon. Common examples include increasing the intensity of sports participation, falling from a height, stepping into a hole.
Symptoms
Whereas calf strains and tendonitis may cause tightness or pain in the leg, Achilles tendon ruptures are typically accompanied by a popping sensation and noise at the time of the injury. In fact, some patients joke that the popping sound was loud enough to make them think they?d been shot. Seeing a board-certified orthopedic surgeon is the best way to determine whether you have suffered an Achilles tendon tear.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of an Achilles tendon rupture can be made easily by an orthopedic surgeon. The defect in the tendon is easy to see and to palpate. No x-ray, MRI or other tests are necessary.
Non Surgical Treatment
Nonsurgical treatment involves extended casting, special braces, orthotics, and physical therapy. Avoids the normal complications and expenses of surgery. Some studies show the outcome is similar to surgery in regard to strength and function. There is risk of an over-lengthened tendon with inadequate tension. Extended immobilization can lead to more muscle weakness. Nonsurgical treatment has a higher incidence of re-rupture than surgical repair. Nonsurgical treatment is often used for nonathletes or for those with a general low level of physical activity who would not benefit from surgery. The elderly and those with complicating medical conditions should also consider conservative nonsurgical treatment. 
Surgical Treatment
While it is possible to treat an Achilles tendon rupture without surgery, this is not ideal since the maximum strength of the muscle and tendon rarely returns. The reason is the ends of the tendon are ruptured in a very irregular manner, almost like the ends of a paint brush. As soon as the tendon ruptures, the calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle) continues to pull on the tendon and the end of the ruptured tendon pulls back into the leg, which is called retraction. Once the tendon retracts, it is never possible to get sufficient strength back without surgery, because the muscle no longer functions at the correct biomechanical length and is now stretched out. There are patients for whom surgery cannot be performed, in particular, due to existing medical conditions that may add to potential for complications following surgery. For these patients, a specially designed boot that positions the foot correctly and takes the pressure and tension off the muscle and tendon is used. Most importantly, a cast is never used because it causes permanent shrinkage (atrophy) of the calf muscle. The special boot permits pressure on the foot with walking. The boot also has a hinge to permit movement of the ankle. Many studies of Achilles tendon ruptures have shown that this movement of the foot in the boot while walking is ideal for tendon healing. If surgery is not recommended, it is essential to obtain special tests to check that the ends of the tendon are lying next to each other so that healing can occur. The best test to do this is an ultrasound and not an MRI.
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Symptoms
Overview
Flatfoot deformity is a general term used to describe a person whose arches are slowly dropping to the ground, aka ?fallen arches.? Adult-acquired flatfoot deformity can be caused by several factors, but the most common is abnormal functioning of the posterior tibial tendon in the foot and ankle. The posterior tibial tendon is the primary tendon that supports the arch. If this tendon begins to elongate from a sustained, gradual stretch over a long period of time, then the arch will progressively decrease until full collapse of the arch is noted on standing. What makes this tendon elongated? Biomechanical instability of the foot such as over-pronation or an accessory bone at the insertion site of the tendon are the primary causes for posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. 
Causes
Obesity - Overtime if your body is carrying those extra pounds, you can potentially injure your feet. The extra weight puts pressure on the ligaments that support your feet. Also being over weight can lead to type two diabetes which also can attribute to AAFD. Diabetes - Diabetes can also play a role in Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity. Diabetes can cause damage to ligaments, which support your feet and other bones in your body. In addition to damaged ligaments, uncontrolled diabetes can lead to ulcers on your feet. When the arches fall in the feet, the front of the foot is wider, and outer aspects of the foot can start to rub in your shoe wear. Patients with uncontrolled diabetes may not notice or have symptoms of pain due to nerve damage. Diabetic patient don?t see they have a problem, and other complications occur in the feet such as ulcers and wounds. Hypertension - High blood pressure cause arteries narrow overtime, which could decrease blood flow to ligaments. The blood flow to the ligaments is what keeps the foot arches healthy, and supportive. Arthritis - Arthritis can form in an old injury overtime this can lead to flatfeet as well. Arthritis is painful as well which contributes to the increased pain of AAFD. Injury - Injuries are a common reason as well for AAFD. Stress from impact sports. Ligament damage from injury can cause the bones of the foot to fallout of ailment. Overtime the ligaments will tear and result in complete flattening of feet.
Symptoms
Often, this condition is only present in one foot, but it can affect both. Adult acquired flatfoot symptoms vary, but can swelling of the foot's inner side and aching heel and arch pain. Some patients experience no pain, but others may experience severe pain. Symptoms may increase during long periods of standing, resulting in fatigue. Symptoms may change over time as the condition worsens. The pain may move to the foot's outer side, and some patients may develop arthritis in the ankle and foot.
Diagnosis
Clinicians need to recognize the early stage of this syndrome which includes pain, swelling, tendonitis and disability. The musculoskeletal portion of the clinical exam can help determine the stage of the disease. It is important to palpate the posterior tibial tendon and test its muscle strength. This is tested by asking patient to plantarflex and invert the foot. Joint range of motion is should be assessed as well. Stiffness of the joints may indicate longstanding disease causing a rigid deformity. A weightbearing examination should be performed as well. A complete absence of the medial longitudinal arch is often seen. In later stages the head of the talus bone projects outward to the point of a large "lump" in the arch. Observing the patient's feet from behind shows a significant valgus rotation of the heel. From behind, the "too many toes" sign may be seen as well. This is when there is abducution of the forefoot in the transverse plane allowing the toes to be seen from behind. Dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon can be assessed by asking the patient to stand on his/her toes on the affected foot. If they are unable to, this indicates the disease is in a more advanced stage with the tendon possibly completely ruptured.
Non surgical Treatment
In the early stages, simple pre-fabricated orthotics can help improve the heel position to reduce the mechanical load which is contributing to the symptoms. In advanced stages or long term orthotic use, a plaster of paris or foam box cast can be taken and specific bespoke orthotics manufactured. If the condition develops further a AFO (ankle foot orthotic) may be necessary for greater control. In more advanced stages of symptomatic Adult Acquired flat feet, where the conservative methods of treatment have failed there are various forms of surgery available depending upon the root cause of the issue and severity. 
Surgical Treatment
A new type of surgery has been developed in which surgeons can re-construct the flat foot deformity and also the deltoid ligament using a tendon called the peroneus longus. A person is able to function fully without use of the peroneus longus but they can also be taken from deceased donors if needed. The new surgery was performed on four men and one woman. An improved alignment of the ankle was still evident nine years later, and all had good mobility 8 to 10 years after the surgery. None had developed arthritis.